Quantitative assessment of GPCR ligand scavenging
bioSens-All® is an enhanced bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (ebBRET)-based biosensor platform that is primarily used for monitoring G protein and β-arrestin signaling dynamics downstream of GPCRs [1]. In a novel application of this technology, bioSens-All® G protein activation biosensors were used to quantify and characterize the chemokine scavenging activity of a chemokine receptor (Figure 1).
At the heart of this new application are two transiently-transfected cell populations: i) HEK-293 SL cell [2] transfected with the chemokine scavenging receptor (i.e., ”scavenger” cells), and ii) HEK-293 SL cells co-transfected with a non-scavenging receptor that responds to the same chemokine, and a biosensor that permits quantification of this receptor’s signaling activity following chemokine stimulation (i.e., “sensor” cells).
In this assay, scavenger cells (cultured in a 96-well microplate) are incubated with a fixed concentration of chemokine for at least 4h at 37°C. Following the scavenging period, culture media from the scavenging cells are transferred directly to sensor cells (cultured in a separate 96-well microplate). Following a 10-minute stimulation period, BRET is recorded from the sensor cell plate. BRET values are then transformed to chemokine concentrations via interpolation from a chemokine dose-response (i.e., “standard”) curve generated with the same sensor cells.
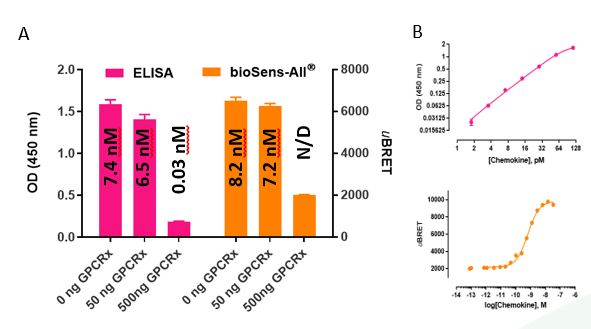 Figure 2: Quantification of chemokine scavenging – comparison of traditional ELISA and bioSens-All®-based methods. (A) Chemokine x concentrations in scavenger cell supernatant were quantified in parallel, by traditional ELISA or bioSens-All®-based methods. (B) The resulting OD (for ELISA) or uBRET (for bioSens-All® assay) values were transformed to chemokine concentrations via interpolation from chemokine standard curves. Data representative from one experiment in which scavenger cells were incubated O/N with 15 nM of chemokine.
Figure 2: Quantification of chemokine scavenging – comparison of traditional ELISA and bioSens-All®-based methods. (A) Chemokine x concentrations in scavenger cell supernatant were quantified in parallel, by traditional ELISA or bioSens-All®-based methods. (B) The resulting OD (for ELISA) or uBRET (for bioSens-All® assay) values were transformed to chemokine concentrations via interpolation from chemokine standard curves. Data representative from one experiment in which scavenger cells were incubated O/N with 15 nM of chemokine.
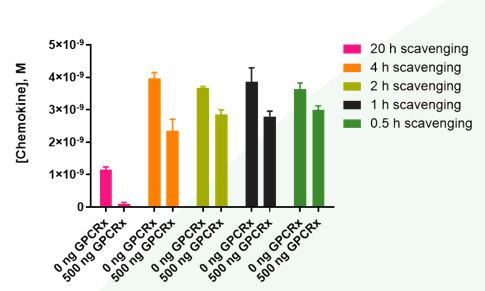 Figure 3: Effects of time on GPCRx-mediated chemokine scavenging. Control (mock)- and GPCRx-transfected scavenger cells were incubated with chemokine (5 nM) for varying amounts of time prior to quantification of chemokine levels via the bioSens-All® assay. At all time points, cells transfected with scavenging receptor GPCRx displayed higher scavenging efficacy than mock-transfected cells. Furthermore, GPCRx-mediated scavenging was time dependent: cells expressing GPCRx scavenged approximately 90% (O/N), 41% (4 h), 22% (2 h), 27% (1 h) and 18% (0.5 h) of the added chemokine versus mock-transfected scavenger cells.
Figure 3: Effects of time on GPCRx-mediated chemokine scavenging. Control (mock)- and GPCRx-transfected scavenger cells were incubated with chemokine (5 nM) for varying amounts of time prior to quantification of chemokine levels via the bioSens-All® assay. At all time points, cells transfected with scavenging receptor GPCRx displayed higher scavenging efficacy than mock-transfected cells. Furthermore, GPCRx-mediated scavenging was time dependent: cells expressing GPCRx scavenged approximately 90% (O/N), 41% (4 h), 22% (2 h), 27% (1 h) and 18% (0.5 h) of the added chemokine versus mock-transfected scavenger cells.
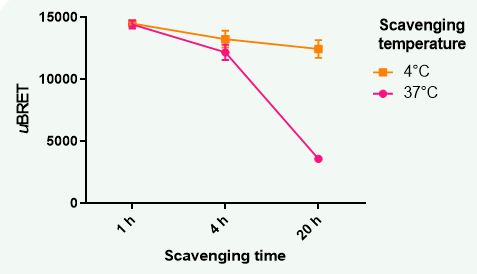 Figure 4: Effects of temperature on GPCRx-mediated chemokine scavenging. GPCRx-transfected scavenger cells were incubated with chemokine (15 nM) at 4°C or 37°C for varying periods of time (1 h – O/N) prior to quantification of chemokine levels via the bioSens-All® assay. Temperature had no impact on residual chemokine levels when the scavenging assay was conducted over a 1 h period. After a 4 h incubation of scavenger cells with chemokine, a temperature effect on scavenging started to become apparent. This effect was dramatically amplified when the scavenging assay was prolonged to overnight (i.e., ~ 20h), with cells incubated at 4°C showing a ~71% decrease in scavenging activity versus those incubated at 37°C.
Figure 4: Effects of temperature on GPCRx-mediated chemokine scavenging. GPCRx-transfected scavenger cells were incubated with chemokine (15 nM) at 4°C or 37°C for varying periods of time (1 h – O/N) prior to quantification of chemokine levels via the bioSens-All® assay. Temperature had no impact on residual chemokine levels when the scavenging assay was conducted over a 1 h period. After a 4 h incubation of scavenger cells with chemokine, a temperature effect on scavenging started to become apparent. This effect was dramatically amplified when the scavenging assay was prolonged to overnight (i.e., ~ 20h), with cells incubated at 4°C showing a ~71% decrease in scavenging activity versus those incubated at 37°C.
Results and Conclusions
The bioSens-All®-based method for quantifying chemokine concentrations produces results that are equivalent to those obtained with a standard ELISA-based technique (Figure 2). Scavenging efficiency is dependent on time, temperature and scavenging receptor expression levels (Figures 3-4), as would be expected for a receptor-mediated scavenging process. Importantly, the bioSens-All®-based approach can be easily completed within 2 h while the ELISA-based method requires at least 24 h. This protocol can be adapted to use different scavenging cells, including primary cells displaying endogenous scavenging receptor expression. The bioSens-All® assay is not limited to the quantification of chemo-/cytokines but can also be applied to quantifying other analytes for which signaling-competent cell surface receptors exist.